Introduction To Computer Networks
Modern world scenario is ever changing. Data Communication and network have changed the way business and other daily affair works. Now, they highly rely on computer networks and internetwork.
A set of devices often mentioned as nodes connected by media link is called a Network.
A node can be a device which is capable of sending or receiving data generated by other nodes on the network like a computer, printer etc. These links connecting the devices are called Communication channels.
Computer network is a telecommunication channel using which we can share data with other coomputers or devices, connected to the same network. It is also called Data Network. The best example of computer network is Internet.
Computer network does not mean a system with one Control Unit connected to multiple other systems as its slave. That is Distributed system, not Computer Network.
A network must be able to meet certain criterias, these are mentioned below:
- Performance
- Reliability
- Scalability
Computer Networks: Performance
It can be measured in the following ways:
- Transit time : It is the time taken to travel a message from one device to another.
- Response time : It is defined as the time elapsed between enquiry and response.
Other ways to measure performance are :
- Efficiency of software
- Number of users
- Capability of connected hardware
Computer Networks: Reliability
It decides the frequency at which network failure take place. More the failures are, less is the network's reliability.
Computer Networks: Security
It refers to the protection of data from any unauthorised user or access. While travelling through network, data passes many layers of network, and data can be traced if attempted. Hence security is also a very important characteristic for Networks.
Properties of a Good Network
- Interpersonal Communication: We can communicate with each other efficiently and easily. Example: emails, chat rooms, video conferencing etc, all of these are possible because of computer networks.
- Resources can be shared: We can share physical resources by making them available on a network such as printers, scanners etc.
- Sharing files, data: Authorised users are allowed to share the files on the network.
Basic Communication Model
A Communication model is used to exchange data between two parties. For example: communication between a computer, server and telephone (through modem).


Communication Model: Source
Data to be transmitted is generated by this device, example: telephones, personal computers etc.
Communication Model: Transmitter
The data generated by the source system is not directly transmitted in the form its generated. The transmitter transforms and encodes the data in such a form to produce electromagnetic waves or signals.
Communication Model: Transmission System
A transmission system can be a single transmission line or a complex network connecting source and destination.
Communication Model: Receiver
Receiver accepts the signal from the transmission system and converts it into a form which is easily managed by the destination device.
Communication Model: Destination
Destination receives the incoming data from the receiver.
Data Communication
The exchange of data between two devices through a transmission medium is called Data Communication. The data is exchanged in the form of 0's and 1's. The transmission medium used is wire cable. For data communication to occur, the communication device must be a part of a communication system. Data Communication has two types - Local and Remote which are discussed below:
Data Communication: Local
Local communication takes place when the communicating devices are in the same geographical area, same building, or face-to-face etc.
Data Communication: Remote
Remote communication takes place over a distance i.e. the devices are farther. The effectiveness of a data communication can be measured through the following features :
- Delivery: Delivery should be done to the correct destination.
- Timeliness: Delivery should be on time.
- Accuracy: Data delivered should be accurate.
Components of Data Communication
- Message: It is the information to be delivered.
- Sender: Sender is the person who is sending the message.
- Receiver: Receiver is the person to whom the message is being sent to.
- Medium: It is the medium through which the message is sent. For example: A Modem.
- Protocol: These are some set of rules which govern data communication.
Types of Topologies
BUS Topology
Bus topology is a network type in which every computer and network device is connected to single cable. When it has exactly two endpoints, then it is called Linear Bus topology.
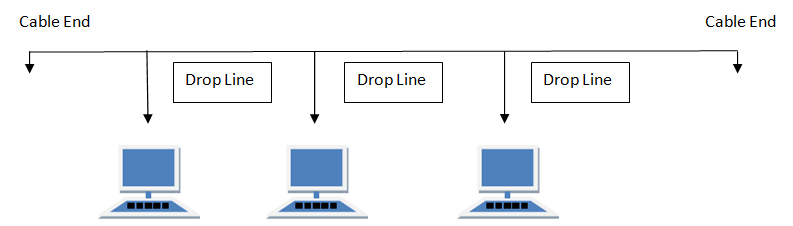
Features of Bus Topology
- It transmits data only in one direction.
- Every device is connected to a single cable
Advantages of Bus Topology
- It is cost effective.
- Cable required is least compared to other network topology.
- Used in small networks.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
- Cables fails then whole network fails..
- Cable has a limited length.
- It is slower than the ring topology.
RING Topology
It is called ring topology because it forms a ring as each computer is connected to another computer, with the last one connected to the first. Exactly two neighbours for each device.
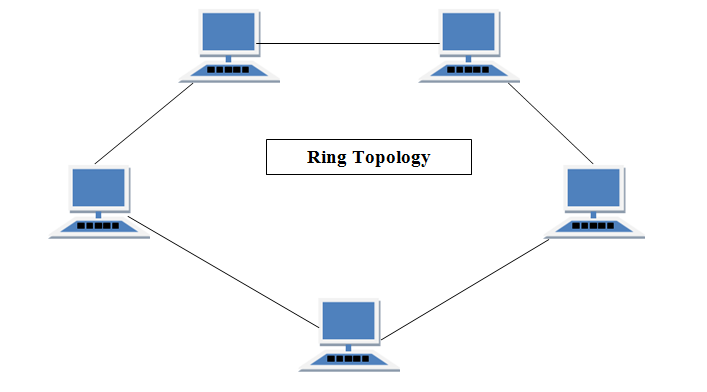
Features of Ring Topology
- A number of repeaters are used for Ring topology with large number of nodes, because if someone wants to send some data to the last node in the ring topology with 100 nodes, then the data will have to pass through 99 nodes to reach the 100th node. Hence to prevent data loss repeaters are used in the network.
- The transmission is unidirectional, but it can be made bidirectional by having 2 connections between each Network Node, it is called Dual Ring Topology.
- In Dual Ring Topology, two ring networks are formed, and data flow is in opposite direction in them. Also, if one ring fails, the second ring can act as a backup, to keep the network up.
- Data is transferred in a sequential manner that is bit by bit. Data transmitted, has to pass through each node of the network, till the destination node.
Advantages of Ring Topology
- Transmitting network is not affected by high traffic or by adding more nodes, as only the nodes having tokens can transmit data.
- Cheap to install and expand
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
- Troubleshooting is difficult in ring topology.
- Adding or deleting the computers disturbs the network activity.
- Failure of one computer disturbs the whole network.
STAR Topology
In this type of topology all the computers are connected to a single hub through a cable. This hub is the central node and all others nodes are connected to the central node.
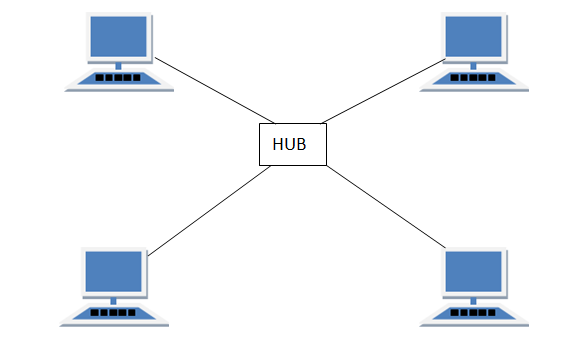
Features of Star Topology
- Every node has its own dedicated connection to the hub.
- Hub acts as a repeater for data flow.
Advantages of Star Topology
- Fast performance with few nodes and low network traffic.
- Hub can be upgraded easily.
- Easy to setup and modify..
Disadvantages of Star Topology
- Cost of installation is high.
- Expensive to use.
- If the hub fails then the whole network is stopped because all the nodes depend on the hub.
MESH Topology
It is a point-to-point connection to other nodes or devices. All the network nodes are connected to each other. Mesh has
n(n-1)/2 physical channels to link n devices.
There are two techniques to transmit data over the Mesh topology, they are :
- Routing
- Flooding
MESH Topology: Routing
In routing, the nodes have a routing logic, as per the network requirements. Like routing logic to direct the data to reach the destination using the shortest distance. Or, routing logic which has information about the broken links, and it avoids those node etc.
MESH Topology: Flooding
In flooding, the same data is transmitted to all the network nodes, hence no routing logic is required. The network is robust, and the its very unlikely to lose the data. But it leads to unwanted load over the network.
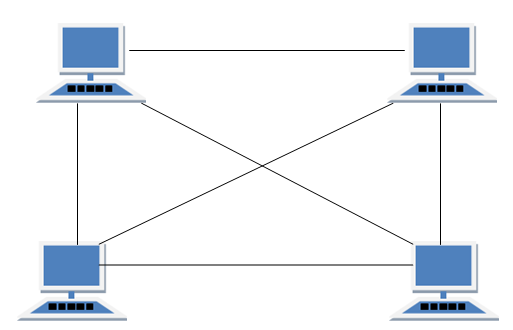
Types of Mesh Topology
- Partial Mesh Topology : In this topology some of the systems are connected in the same fashion as mesh topology but some devices are only connected to two or three devices.
- Full Mesh Topology : Each and every nodes or devices are connected to each other.
Features of Mesh Topology
- Fully connected.
- Robust.
- Not flexible.
Advantages of Mesh Topology
- Each connection can carry its own data load.
- Fault is diagnosed easily.
- Provides security and privacy.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Installation and configuration is difficult.
- Cabling cost is more.
- Bulk wiring is required.
TREE Topology
It has a root node and all other nodes are connected to it forming a hierarchy. It is also called hierarchical topology. It should at least have three levels to the hierarchy.
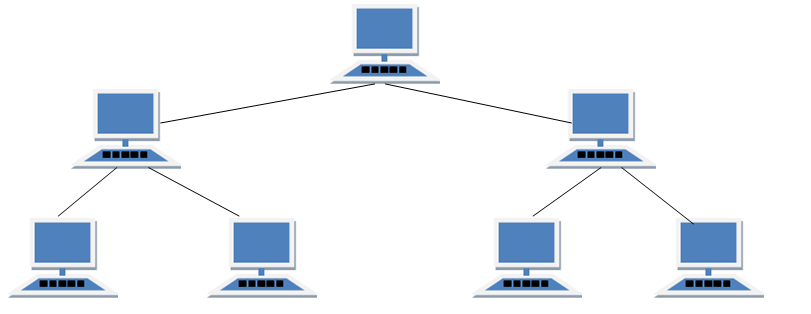
Features of Tree Topology
- Ideal if workstations are located in groups.
- Used in Wide Area Network.
Advantages of Tree Topology
- Extension of bus and star topologies.
- Easily managed and maintained.
- Error detection is easily done.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology
- Heavily cabled.
- Costly.
- If more nodes are added maintenance is difficult.
- Central hub fails, network fails.
HYBRID Topology
It is two different types of topologies which is a mixture of two or more topologies. For example if in an office in one department ring topology is used and in another star topology is used, connecting these topologies will result in Hybrid Topology (ring topology and star topology).
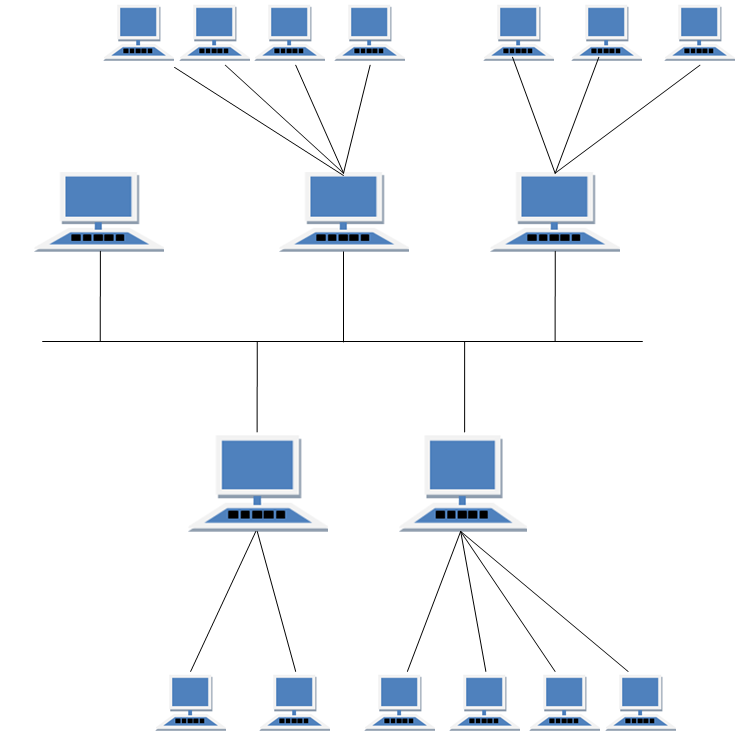
Features of Hybrid Topology
- It is a combination of two or topologies
- Inherits the advantages and disadvantages of the topologies included
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
- Effective.
- Scalable as size can be increased easily.
- Flexible.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
- Complex in design.
Business Computer
Following are some business applications of computer networks:
1. Resource Sharing:
The goal is to make all programs, equipments(like printers etc), and especially data, available to anyone on the network without regard to the physical location of the resource and the user.2. Server-Client model:
One can imagine a company's information system as consisting of one or more databases and some employees who need to access it remotely. In this model, the data is stored on powerful computers called Servers. Often these are centrally housed and maintained by a system administrator. In contrast, the employees have simple machines, called Clients, on their desks, using which they access remote data.3. Communication Medium:
A computer network can provide a powerful communication medium among employees. Virtually every company that has two or more computers now has e-mail (electronic mail), which employees generally use for a great deal of daily communication4. eCommerce:
A goal that is starting to become more important in businesses is doing business with consumers over the Internet. Airlines, bookstores and music vendors have discovered that many customers like the convenience of shopping from home. This sector is expected to grow quickly in the future.The most popular forms are listed in the below figure: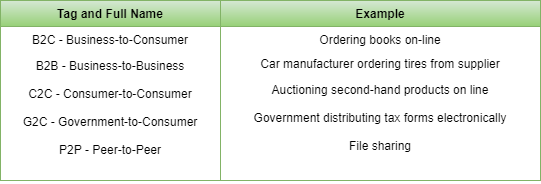
Computer Networks: Home Applications
Some of the most important uses of the Internet for home users are as follows:- Access to remote information
- Person-to-person communication
- Interactive entertainment
- Electronic commerce
Computer Networks: Mobile Users
Mobile computers, such as notebook computers and Mobile phones, is one of the fastest-growing segment of the entire computer industry. Although wireless networking and mobile computing are often related, they are not identical, as the below figure shows.
 The IBM 650 Magnetic Drum Calculator
The IBM 650 Magnetic Drum Calculator Grayson Kirk, President of Columbia University (right) and Kenneth M. King, director of the University's new Computer Center, 1963, in the machine room at the IBM 7090 console, "one of the largest computers in existence" at the time.
Grayson Kirk, President of Columbia University (right) and Kenneth M. King, director of the University's new Computer Center, 1963, in the machine room at the IBM 7090 console, "one of the largest computers in existence" at the time.
 Installation of the IBM 360/91 in the Columbia Computer Center machine room in February or March 1969. Photo: AIS archive.
Installation of the IBM 360/91 in the Columbia Computer Center machine room in February or March 1969. Photo: AIS archive. 
